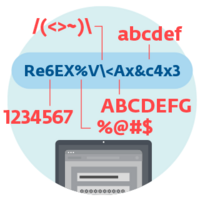
How does ransomware work?
There are multiple techniques used by ransomware cybercriminals including:
- Screen locker ransomware blocks access to the device’s screen other than the malware’s user interface.
- PIN locker ransomware changes the device’s PIN code, rendering its content and functionality inaccessible.
- Disk coding ransomware encrypts the MBR (Master Boot Record) and/or critical file system structures, and thus prevents the user from accessing the operating system.
- Crypto-ransomware encrypts user files stored on disk.
Warning

Why should SMBs care about ransomware?
According to the Ponemon 2017 State of Cybersecurity in Small & Medium-Sized Businesses (SMB) survey, every other company in the poll had experienced a ransomware attack in the previous 12 months, some on multiple occasions. Most (79%) saw their systems infiltrated due to social engineering attacks.
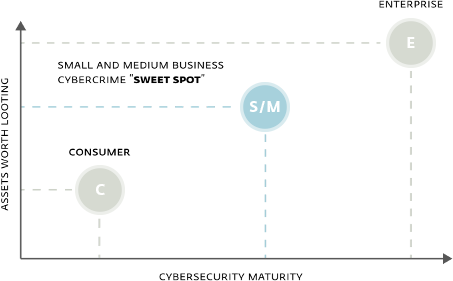
These statistics document two things:
1. Contrary to their own beliefs, SMBs are becoming an increasingly interesting target for cybercriminals.
2. SMBs are more valuable targets for cybercriminals than consumers, and more vulnerable than large enterprises, as small and medium businesses typically lack the financial and information security resources of their corporate counterparts. This combination represents a “sweet spot” for the attackers.
Read more
How to keep your organization protected?
Basic prevention and recovery steps:
- Backup data on a regular basis and keep at least one full backup of the most valuable data off-line
- Keep all software and apps – including operating systems – patched and updated
- Use a reliable, multilayered security solution and make sure it is patched and up-to-date
Additional protective measures
No business is completely safe from ransomware
If your company has not been hit by ransomware you might be tempted to assume this threat is reserved for larger organizations. The statistics show you’d be wrong. Also, a targeted attack can get out of control and cause indiscriminate damage, even worldwide. In June 2017, a malware attack in Ukraine, detected by ESET as Diskcoder.C (aka Petya or NotPetya), soon burrowed its way out of the country. It later transpired this was a well-orchestrated supply-chain attack that infiltrated popular accounting software to attack and harm Ukrainian organizations which got out of hand, infecting many global and smaller companies, causing hundreds of millions of USD in damage.
Another ransomware worm detected by ESET as WannaCryptor.D (aka WannaCry) spread rapidly, using the leaked NSA tool EternalBlue, which exploited a vulnerability in the SMB (Server Message Block) network protocol, mainly used to provide shared access to files and printers. Despite Microsoft issuing patches for most of the targeted, vulnerable Windows OSes almost two months prior to the attack, WannaCryptor.D infiltrated networks in thousands of organizations worldwide. The cost of the damage resulting from this cyberattack has been estimated in billions of USD.
ESET security protects against ransomware
ESET PROTECT
Advanced
Protect your company computers, laptops and mobile devices with security products all managed via a cloud-based management console. The solution includes cloud sandboxing technology, preventing zero-day threats and ransomware, and full disk encryption capability for enhanced data protection.